PROCESS SAFETY SERVICES
Process Safety is an interdisciplinary engineering domain that focuses on the study, prevention, and management of large-scale fires, explosions, and chemical accidents in process plants or other facilities dealing with hazardous and flammable materials. These facilities can include refineries, oil and gas production installations, and other industrial sites where hazardous and flammable substances are handled.

1.Hazard Identification and Risk Analysis (HIRA)
Hazard Identification and Risk Analysis (HIRA) includes all activities involved in identifying hazards, understanding potential incident scenarios, identifying safeguards and evaluating risk to people, the environment, property and business. HIRA encompasses the entire spectrum of risk analysis, from qualitative to quantitative. The purpose of HIRA is to identify, evaluate, and reduce the likelihood and/or minimize the consequences of uncontrolled releases and other safety or environmental incidents within the organization’s risk tolerance criterion by recommending appropriate prevention and/or mitigation measures.
2.Quantitative Risk Assessment
Quantitative Risk Assessment (QRA) is a powerful tool for systematicallysystematic approach for analyzing and managing risks, helping organizations to make informed and data-driven decisions to minimize potential adverse outcomes. This method involves the use of numerical values and statistical techniques to estimate the probability of different adverse events and the magnitude of their consequences. This is not only applicable in industrial processes, equipment failure, chemical spills, pollution and natural disasters but also equally important for finance and health care sectors.

METHODOLOGY
.png)
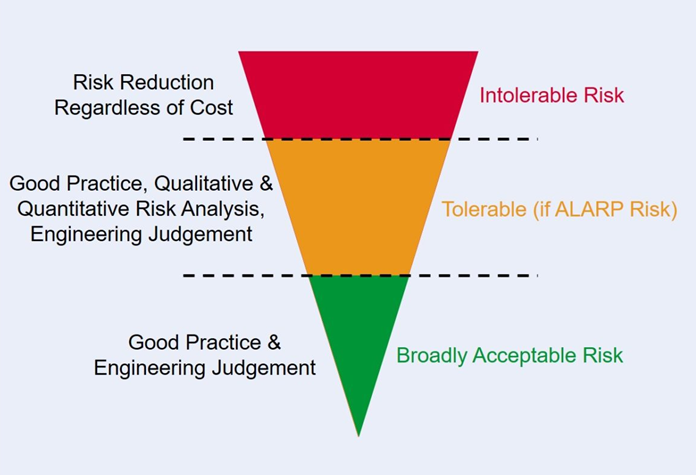
3.As Low As Reasonably Practicable (ALARP)
It’s a principle used in the regulation and management of safety-critical systems. The idea is to reduce the risk to a level that is as low as reasonably practicable, meaning that the cost, time, and effort involved in further reducing the risk would be grossly disproportionate to the benefit gained.
4.Process Hazard Analysis (PHA)
-
Process Hazard Analysis (PHA) is a systematic approach used to identify and evaluate potential
hazards
associated with industrial processes. The primary goal of PHA is to prevent accidents and
enhance
overallprocess safety by proactively managing and mitigating risks.
- Improved Safety: Helps in preventing accidents and protecting workers and the environment.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures compliance with safety regulations, such as OSHA’s Process Safety Management (PSM) and OISD standards, PNGRB Regulations.
- Sustainable Practices: It promotes sustainable practices by ensuring that processes are designed and operated safely.
- Crisis Management: Effective hazard management reduces the likelihood of incidents that could damage the organization’s reputation.
Benefits of PHA:

.jpg)
5.Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) Study
HAZOP is a detailed and systematic technique used to identify potential hazards
and
operability problems in a process or system. It focuses on deviations from the design intent
that could lead
to hazardous situations.
Methodology:
- Guidewords: Uses specific guidewords (e.g., “No,” “More,” “Less,” “As well as”) to systematically examine each part of the process.
- Multidisciplinary Team: Involves a team with diverse expertise to ensure comprehensive analysis.
- Detailed Analysis: Examines each process step to identify deviations and their potential consequences.
Hazard Identification (HAZID) Study
HAZID is a proactive approach used to identify potential hazards early in the
design or
operational phase of a project. It aims to uncover all possible hazards, including those that
may not be
immediately apparent.
Methodology:
- Scenario Analysis: Considers various scenarios to identify hazards and deviations from normal operating conditions.
- Broad Scope: Typically performed at an early stage to assess a wide range of hazards and their potential causes and consequences.
- Multidisciplinary Team: Involves experts from different fields to ensure a thorough assessment.
.jpg)

6.Emergency Response and Disaster Management Plan (ERDMP)
The Emergency Response and Disaster Management Plan (ERDMP) Regulations, 2010 were established by the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) in India. These regulations provide a comprehensive framework for managing emergencies and disasters in the petroleum and natural gas sector.
7.On-site Emergency Plan
An on-site emergency plan is designed to handle emergencies that occur within
the premises
of a facility. The key elements include:
The key elements include:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying potential hazards and assessing the risks associated with them.
- Emergency Procedures: Detailed steps to be taken during an emergency, including evacuation routes, emergency shutdown procedures, and first aid measures.
- Roles and Responsibilities: Assigning specific roles to personnel, such as incident controllers and emergency coordinators.
- Communication: Establishing clear communication channels within the facility to ensure timely dissemination of information.
.jpg)
.jpg)
Off-site Emergency Plan
An off-site emergency plan is designed to manage emergencies that extend beyond
the
facility’s premises and may impact the surrounding community.
The key elements include:
- Coordination with Authorities: Collaborating with local authorities, emergency services, and community organizations.
- Public Information: Informing the public about potential hazards and the actions they should take during an emergency.
- Evacuation Plans: Developing evacuation plans for the surrounding areas, including transportation and shelter arrangements.
- Medical Support: Ensuring that medical facilities are prepared to handle casualties and provide necessary treatment.
8.Hazardous Area Classification (HAC)
Hazardous Area Classification (HAC) is a critical safety assessment used to
identify and
document areas within a facility where there may be a flammable or explosive atmosphere. This
classification
helps in determining the necessary precautions to prevent ignition sources that could lead to
fires or
explosions.
Methodology:
- Identify point sources
- Determine grade of release
- Determination of fluid category
- Establish zone classification
- Determine hazard radius
- Determine Gas Group and Temperature Class
- Zone Marking on the Layout






